Collaborative practice is the process whereby members of different professions and/or agencies work together to provide integrated health and/or social care for the benefit of service users (Pollard et al, 2005: 10).
As much as a decade ago the Department of Health (DoH) published a consultation document outlining a review of National Health Service (NHS) workforce planning, in which recommendations were made that interprofessional practice (IPP) be more widely adopted for the benefit of service users (Department of Health, 2000a). Since then the concept has developed and now extends beyond the medicine and nursing professions to include other healthcare professions. The new initiatives meant major cultural changes within the NHS; staff that had been used to working uniprofessionally had to embrace a new culture of mutual respect and shared values (Pollard et al, 2005).
Various terms are used to describe collaborative practice within the healthcare setting; interprofessional is the term that is commonly used specifically to describe interaction between professionals with common goals in working together (Leathard, 2009) Authors will also use the terms, intraprofessional and multiprofessional and in some texts multidisciplinary is used to describe collaborative practice. Whatever term is used the common theme is that they all refer to styles of work undertaken by professionals.
Being professional
In order to be recognized as a member of a profession every professional practitioner will have undergone training and achieved a standard set by their professional body. However, being professional is more than just achieving a qualification, it is also about having values, both moral and ethical. On the subject of professional values Crowley (2006: 139) states, ‘professional values are beliefs and attitudes about the worth of the profession. They guide behaviour and endorse standards of conduct that are professionally acceptable’.
Many professions are regulated and members of the public who use the services that these professionals provide expect them to adhere to published standards of conduct and practice. All professions will have the same basic features:
- Assured standards of training and qualification
- A code of professional conduct
- A commitment to maintain competence
- Sanctions for those who transgress
- Practitioners held in high public regard.
By becoming self regulated, veterinary nurses in the UK have demonstrated to the public (the clients), that they are willing to set and meet standards of professional conduct, and maintain professional skills and knowledge. The Royal College of Veterinary Surgeons' (RCVS) Guide to Professional Conduct for Veterinary Nurses (2010) sets the basic principles for the professional behaviour expected of a veterinary nurse in the UK.
The main purpose of regulation is to protect the public (in the case of the veterinary profession, clients and their pets) from those that are unfit to practise. All regulated professions, for example, lawyers, accountants, doctors or nurses, have mechanisms in place to prevent those that fall below the accepted standard from practising. Veterinary nurses, just as other professionals, have a duty to be publically accountable for their actions and be confident that they can justify their decision making.
Accountability brings benefits for veterinary nurses as they are more likely to be respected as fellow professionals within the veterinary team. They will have more opportunities to lead and develop veterinary nursing as a discipline and as a result will have their skills and status recognized by clients and members of the public.
Achieving IPP
Successful IPP relies on the combination of a number of factors but in particular a certain level of commitment and mutual respect from each of the contributing professions. Individuals need to remain motivated and willing to work towards a common goal but this presupposes that they are both competent and confident to take on their roles within the team. Furthermore, as in any busy work environment, good, open and honest communication is vital.
Competencies that are considered fundamental to being a successful interprofessional practitioner have been succinctly described by Copperman et al (2009: 23) as follows:
‘Knowledge
- Understand the role and working context of other practitioners and begin to identify how these interrelate
- Recognize the range of knowledge and skills of all other colleagues
- Understand the principles and practice of effective teamwork Skills
- Apply sound verbal and written communication methods with colleagues from other work settings
- Identify situations where collaboration is helpful or essential
- Work collaboratively with service users and carers
- Use interprofessional learning in work settings Attitudes
- Appreciate the value of interprofessional collaboration
- Acknowledge and respect others' views, values and ideas.'
Restrictions or limitations to IPP
The introduction of change in any area of life is often met with resistance due to a fear of the unknown and uncertainty about how the changes will affect routines, so it is not surprising that collaborative practice and a new style of working within the NHS has been slow to advance (Caldwell and Atwal, 2003). For IPP to be effective the participants must acknowledge the constraints that could limit its success and work towards overcoming these issues if possible.
One of the most significant limiting factors is the differences between professions and their professional values, ideologies or goals. Traditionally nursing is thought of as a profession with a focus on caring, while the doctors' role is that of curing, each seeing the patient from an independent but different perspective and this in itself may limit participation in interprofessional discussion (Kenny, 2002). Additional limitations to IPP have been described by Leathard (2009) and include the following:
- Practitioners isolated with little management support
- Inequalities in status and pay
- Separate training backgrounds
- Time consuming consultation
- Conflicting professional and organizational boundaries and loyalties
- Differing leadership styles
- Lack of clarity about roles and latent prejudices
(Marshall et al, 1979; Ovretveit, 1990; McGrath, 1991 cited in Leathard, 2009: 7).
Supporting effective collaboration
Barrett and Keeping (2005) discuss both the positive and negative factors that influence the process of collaborative working and in addition consider methods by which support can be provided to increase the likelihood of successful collaboration as follows:
- Reflection and supervision
Self reflection coupled with supervision will assist staff in identifying training and development needs in relation to the knowledge, skills and attitudes required for effective IPP.
- Evaluation
It is essential to evaluate the collaboration process and assess the effectiveness of IPP on a regular basis to ensure all group members are working to the same aims and goals. Group meetings also provide an opportunity to discuss and manage areas of conflict that may arise between professions.
- Interprofessional education (IPE)
The Centre for the Advancement of Interprofessional Education (CAIPE) defines IPE as: ‘Interprofessional education occurs when two or more professions learn with, from and about each other to improve collaboration and the quality of care’ (Centre for the Advancement of Interprofessional Education, 2002)
IPE is recognized as the key to cultivating good collaborative practice and veterinary educators now realize the importance of advancing their students' skills in this area of practice focusing on communication and team-working skills, which helps to foster an understanding and respect for team members' roles. Additionally, learning needs to continue after graduation and professionals are aware that learning and development is an ongoing process, however, support may be required to facilitate this lifelong learning. CAIPE is a resource accessible internationally that offers support with interprofessional learning:
- Reinforcement of professional identity
A fear of losing one's professional identity is considered to be one of the reasons why IPP fails as roles and professional boundaries may change with new working practices. A positive professional identity can be sustained by reinforcing allegiance to individual professional representative organizations for meetings and congresses
- Managerial support
Pertinent managerial or supervisory support can foster team building and enable respect and trust to develop between team members. Managers can assist with training and give clear guidance regarding roles and responsibilities and how they might overlap.
Adapting the concept to the veterinary professions
In recent years the perception of veterinary nursing as a profession in its own right has been more widely acknowledged, with roles for nurses who choose to specialize in one particular area of work being developed. It is not uncommon to find nurses in larger practices that work in only one specific area of a practice; postgraduate qualifications have allowed veterinary nurses to develop specific skills in anaesthesia, critical care and radiography for example. Furthermore, in the future with the development of this model of specialism within veterinary nursing the ‘team’ approach to patient care will become more likely as the value of nurses' skills and experience is recognized.
One of the factors that limit the delivery of interprofessional care within the healthcare setting is poor or untimely communication between multiple professions. Doctors and nurses are central in providing patient care in the short term, however long-term recovery requires coordination of additional services provided by allied health professionals such as physiotherapists, occupational therapists and social workers. Moreover the collaborative field may widen further in some cases to involve lawyers, police and probation officers (Figure 1a and 1b).
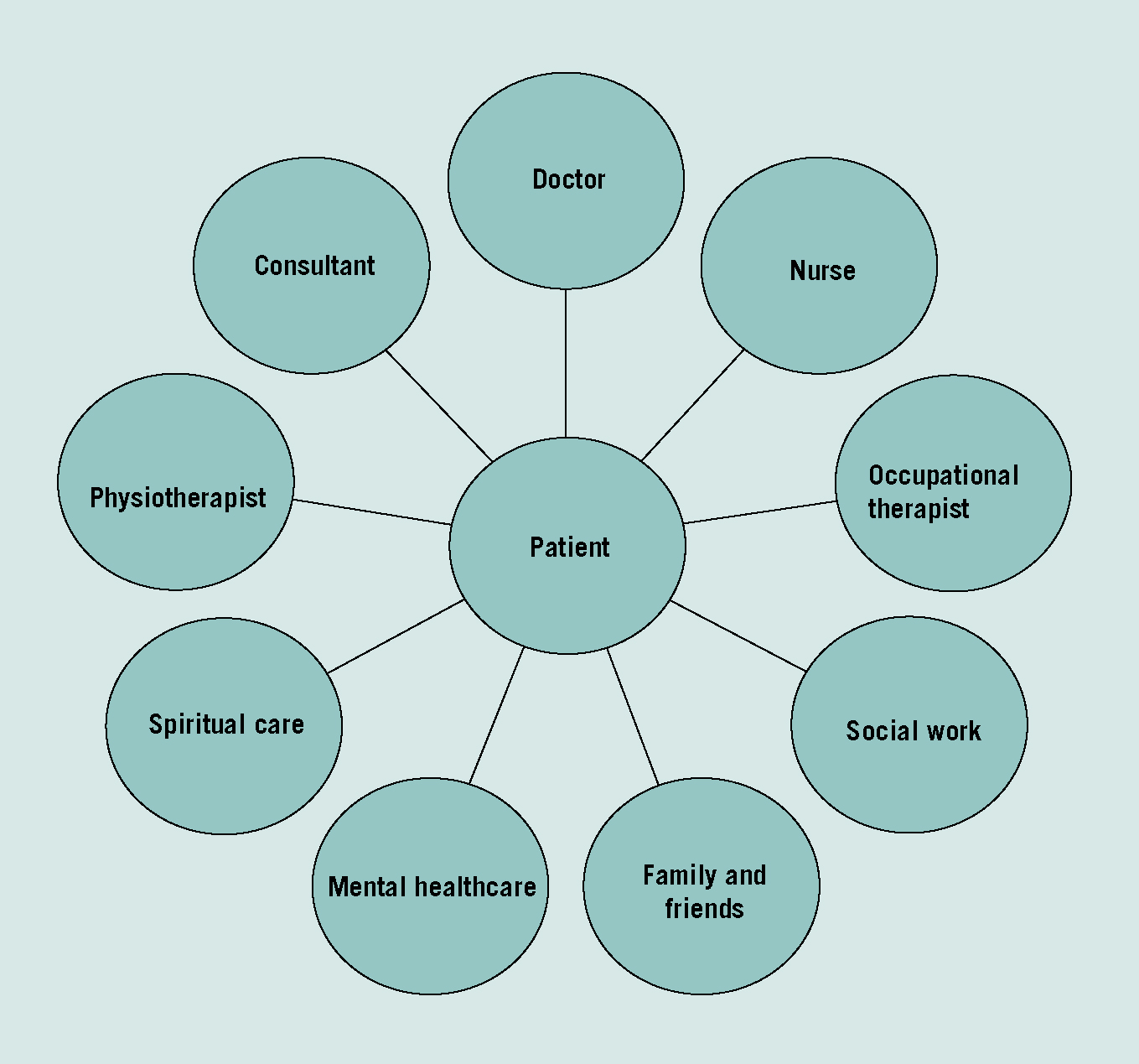
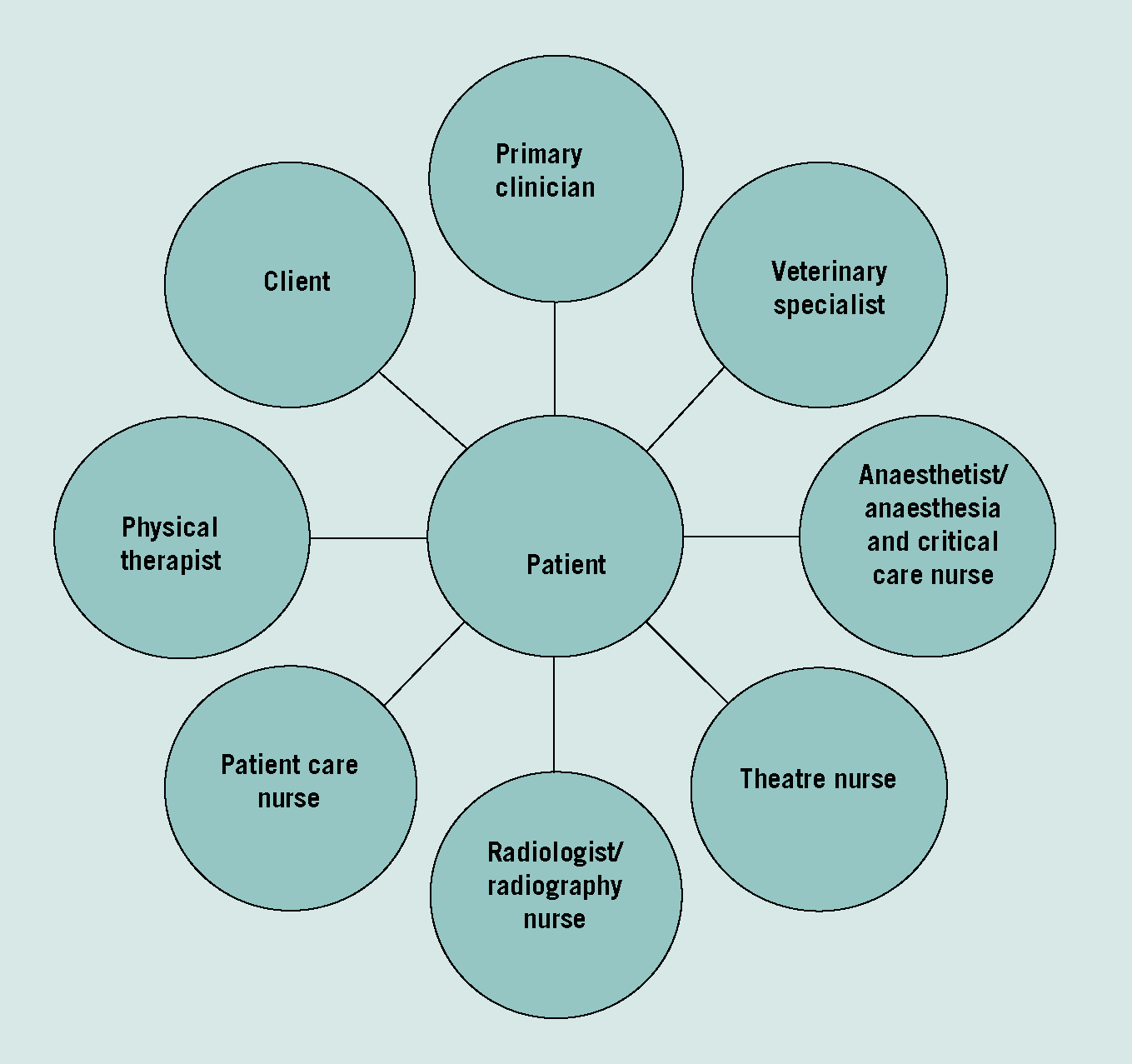
By comparison, in the veterinary setting not only are fewer professions and services involved in providing patient care, but the patient numbers that each organization are caring for are smaller. From this one could make the assumption that IPP in the veterinary setting should be easier to achieve; the positive aspects of IPP are clear with the most obvious advantage being better provision of services (patient and client care) leading to better job satisfaction and more efficient use of staff. It has been concluded from studies in health care that the advantages of interprofessional working generally out weigh the acknowledged disadvantages (McGrath, 1991 cited in Leathard, 2009: 9). These advantages should be sufficient impetus for veterinary nurses, surgeons and allied professionals such as animal physiotherapists and farriers among others, to instigate this way of working.
In practice, even if only on a small scale it should be possible to achieve a certain level of IPP. Nurses can, and should, take the lead role in discussing any nursing considerations that they feel will benefit the patients in their care; time spent in case discussions and sharing ideas, however brief but on a regular basis, will give both sides a better understanding of the patient's progress.
The future for the veterinary professions with regard to collaborative practice is positive, the value of interprofessional education and training is now acknowledged by veterinary institutions and teaching establishments. Veterinary and veterinary nursing undergraduates are being taught interprofessional skills such as team working, communication and decision making concurrently, which leads to a better understanding of each other's roles and responsibilities. New graduates from both professions will expect to work with their colleagues at an interprofessional level.
The veterinary nursing profession is acknowledged to be a young profession, however it is constantly growing in stature with veterinary nurses at the forefront of developing their own professional practice. The value of evidence-based decision making in nursing has been widely recognized by many authors (Kitson, 1997) and it is vital that veterinary nurses now work towards supplementing their own evidence base to inform future veterinary nursing practice.
Conclusion
The future of IPP relies on each discipline developing its own clear identity and skills (Barr, 2000 cited in Kenny, 2002: 68). Professional development for nurses will naturally occur as a result of collaboration between professions and it would be hoped that in this exchange of ideas ‘the humanistic focus of nursing’ will make an effective contribution to patient care (Kenny, 2002).
As documented, higher levels of patient care can be achieved through interprofessional collaboration using a team approach in veterinary practice. However for this concept to be furthered veterinary nurses must be assured in their professionalism and confident in their skills so that they can independently understand their patient's needs, make informed decisions regarding the implementation of nursing care and then reflect on the outcomes using this to inform further decision making.
Key Points
- High levels of patient care can be achieved through interprofessional practice
- Knowledge, skill and an understanding of professional values are required in order to become a successful interprofessional practitioner.
- Interprofessional education is a significant factor in increasing awareness of other professions.
