A 7-month-old domestic short-haired male neutered cat presented at the hospital after a suspected fall from a first floor window. The owner reported that Crumble was an indoor cat, found outside in the morning vomiting, and as there was no other way injuries could have occurred, they concluded he had fallen from an open window on the first floor.
Uroabdomen is most likely caused by abdominal trauma (Fossum, 2009), in this case caused by a fall. As in this case, many blunt traumas cause a bladder rupture (Findji, 2012).
Abdominocentesis is often the best way to confirm a diagnosis of uroabdomen (Kellett-Gregory, 2020). Stabilisation of the patient before repair is vital, including managing hyperkalaemia, metabolic acidosis, azotaemia, hypotension and pain.
Crumble was anaesthetised for surgery to perform a repair of a c-shaped tear in the apex of the bladder. Once this was repaired his abdomen and bladder was also flushed. Further surgical considerations were hypotension, as well as hypothermia, sepsis and hypovolemia. Crumble continued use of intravenous crystalloid fluids (Hartmann’s), noradrenaline, antimicrobials and multi-modal analgesia and Bair Hugger (3M) to help with these.
History
Clinical examination found tachypnoea, mild dyspnoea, pale pink mucus membranes, a capillary refill time of 2 seconds, heart rate (HR) 150 bpm, clear chest auscultation, no obvious fractures, abdominal discomfort on palpitation, ocular examination was normal and Crumble was ambulatory.
He was admitted at 09:05 for further investigations and analgesia, starting with methadone 0.3 mg/kg, and started on fluid bolus 10 ml/kg over 15 minutes. Crumble’s temperature was 36.3°C, so a Bair Hugger heater was used to correct hypothermia. Staff were unable to read blood pressure (BP) on both an oscillometric machine and a doppler monitor. There was poor pulse quality. Mentation remained responsive but quiet. Bloods were taken and showed azotaemia with elevated creatinine levels and hyperkalaemia >12.0 mmol/l (3.8-5.8 mmol/l), pH 7.06 (7.25-7.40), decreased base excess -16 mmol/l and normal lactate, suggesting metabolic acidosis caused by severe uremia. Sodium bicarbonate was sourced from a local referral centre to correct acidosis. Calcium gluconate dose was calculated but not given at 1 mg/kg/15 minutes. Fluid boluses were repeated and intraveous fluid therapy (IVFT) was changed from Hartmann’s solution to saline solution.
Crumble continued on the 32 ml/hour fluid rate and bloods were repeated at 90 minutes from the first sample at 10:30. Crumble remained acidotic with pH 7.07 and hyperkalemic with potassium 5.6 mmol/l (2.9-4.2 mmol/l). Calcium gluconate was not administered, but heart rate and rhythm continued to be monitored using electrocardiograph (ECG). Crumble remained painful in the abdomen, so the decision was made to increase his analgesia. Additional methadone was given (0.2 mg/kg). A urinary catheter was placed and ultrasound scan performed. The ultrasound scan showed fluid in the abdomen. At this time Crumble remained unstable for any anaesthetic. 70 ml serosanguinous fluid was drained from the abdomen using a 23-gauge butterfly catheter consciously guided by ultrasound scanner. After draining the fluid it was then decided to start him on co-amoxiclav 20 mg/kg in case of bowel leakage and the likelihood of urine in the abdomen. A blood pressure reading was repeated using doppler showed a reading of 68 mmHg. Crumble remained on 32 ml/hour fluids to manage any hypovolemia.
Crumble had repeated bloods after another 90 minutes at 12:10, potassium was now stable at 5.3 and pH 7.14. After speaking with an emergency and critical care referral team, it was decided no sodium bicarbonate was required at this time. He was continued on 32 ml/hour intravenous fluids, but remained hypotensive and was unable to get a BP reading, so the decision was made to give a bolus of Gelofusine 5 ml/kg/15 minutes. Radiographs were performed but limited because of pain. They showed a small volume pleural effusion; however, it was not drained as pain was still not managed and breathing remained stable. On the radiographs there were no clear fractures of lower limbs or pelvis, although this was unable to be ruled out at this time because of limited views. Crumble was still tachycardic and tachypnoeic, as well as painful, so he was then started on fentanyl continuous rate infusion (CRI) at 3 mcg/kg/hour.
The owner opted to keep Crumble at the hospital rather than move to a referral clinic because of transport issues. The owner was keen to go ahead with surgery to find the rupture. After the hospital veterinary surgeon had spoken to the referral clinic, Crumble was given American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) grade 5 moribund. While preparing for surgery, Crumble was started on norepinephrine (noradrenaline) CRI to help with ongoing hypotension, as there was no improvement after Gelofusine. Induced anaesthesia with alfaxalone 2 mg/kg was given at 13:35. Endotracheal intubation was performed with a single use PVC endotracheal tube. Intravenous fluids were continued at 4 ml/kg/hour, fentanyl CRI at 4 ml/kg/hour and norepinephrine at 2 ml/kg/hour. Chlorhexidine diluted with water (50:50 ratio) was used as skin preparation. Lidocaine 0.2 ml (lignocaine) was administered along the midline for incision. His temperature on induction was 36.7°C and recovery foil was wrapped around the limbs, a Bair Hugger and heated table were used to try to combat hypothermia.
Anaesthetic was maintained on isoflurane gas. When maintained on 1.5% isoflurane HR 180-200 bpm with normal ECG trace and respiratory rate (RR) was stable at 40 rpm. When the volatile agent was lowered, HR would increase over 200 bp and pupillary reflex would return as well as jaw tone. Therefore, isoflurane gas was kept at 1.5%. Crumble’s mucus membrane remained white with no capillary refill time, and his BP was not able to be read. End tidal CO2 (ETCO2) reading was between 20-30 mmHg while on 3 litres/minute, this decreased further when the flow rate was increased to 5 litres/minute. ETCO2 eventually stopped reading due to a machinery error, and intermittent positive pressure ventilation (IPPV) was given for 10 minutes when Crumble became apnoeic.
The operating surgeon found a c-shaped tear in the bladder, necrotic serosa, uro/haemoabdomen which was suctioned, necrotic tissue debrided and the bladder repaired using a monofilament synthetic polyester suture material (biosyn). At 14:25, bloods were repeated intra-operatively: pH increased to 7.16, potassium increased to 6.5 mmol/l, ionised calcium decreased to 1.11 mmol/l. The abdomen was flushed with 500 ml of warmed saline, this caused the body temperature to decrease to 36.5°C. A BP of 38 mmhg was obtained using a Doppler and, noradrenaline CRI was increased to 5 ml/kg/hour. The urinary catheter was replaced with an adjustable urinary catheter (KatKath), flushed with warmed sterile saline to ensure the bladder repair was secure and a collection bag was attached.
At 15:50 a fourth blood sample was taken: potassium 5.5 mmol/l, ionised calcium 1.14 mmol/l, creatinine 365 mg/dl. Crumble recovered from his anaesthetic quickly, but he became hypothermic in recovery with a temperature of 35.4°C. Crumble’s HR was 180 bpm, RR 40 and the mucus membrane was white with no refill time. Crumble recovered in kennel with IVFT and both CRIs continued, foil was removed from the limbs and Bair Hugger remained on to help with hypothermia. At 16:30 Crumble was up and moving around his kennel. BP with doppler was 40 mmHg with noradrenaline 4 ml/kg/hour. At 17:00 pain scored 6-7/20 on the Glasgow pain score, so fentanyl was increased to 4 mcg/kg/hour to help manage pain. Urine was leaking around the catheter. Ultrasound of bladder was performed to ensure it remained in place - this showed that the catheter remained in - and it was flushed. At 19:00 BP was 116 mmHg and stable, Crumble was comfortable on fentanyl CRI and looking bright in his kennel.
Crumble was closely observed overnight. His BP remained stable and he stopped the noradrenaline the following morning. Bloods were repeated and showed pH 7.37 and creatinine 180 mg/dl. Crumble’s biochemistry results improving, along with the fact that he had eaten well on recovery, meant that the decision was made to administer non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (meloxicam) at this point. Analgesia for cats can be limited to NSAIDs and opioids. Crumble had returned to normothermic, and his checks showed he had good peripheral pulses, HR 160, mucus membrane was pale pink and refill 1.5 seconds, RR 28 and he was purring. At 13:00 it was decided to stop fentanyl and remain on methadone (Comfortan) at 4 mg/kg, to then change to buprenorphine (Vetergesic) 0.02 mg/kg. At 16:00 the urinary catheter was removed. Following this, at 16:15 5.4 ml of urine was passed in the litter tray. The clinical plan was to remain in overnight and monitor urine output and pain.
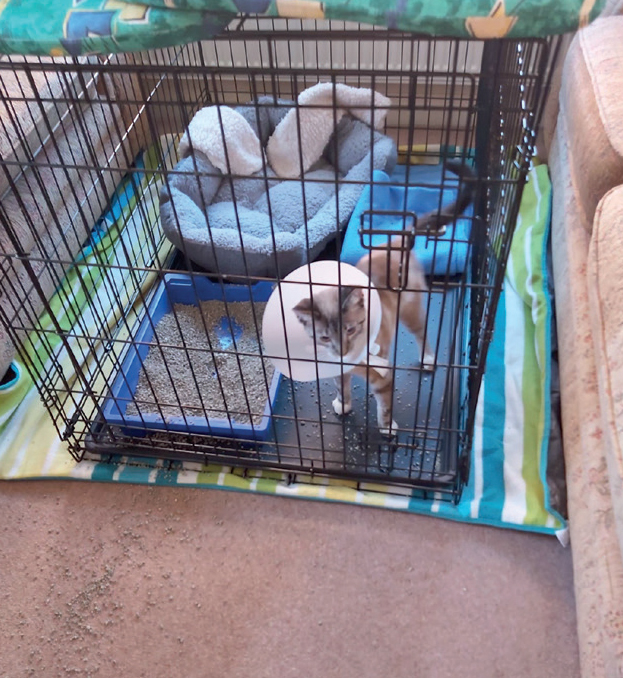
On the third day in hospital Crumble’s check showed he remained bright, his pain score was low, he was passing urine in tray well and eating (Figure 1). Following this he was discharged with oral meloxicam (Loxicom), oral amoxicillin (Synulox) and sublingual Vetergesic, with the owner to monitor closely at home on cage rest (Figure 2), and a review at an appointment in 24-48 hours.

Discussion
On arrival, methadone 0.3 mg/kg was administered, as a full agonist the opioid is good for pain management in cats (Harvey and Tasker, 2013). Crumble was likely metabolic acidotic although PCO2 was within the normal range (King and Boag, 2018). Severe metabolic acidosis <7.2 can be treated by administering bicarbonate (kg x BE x 0.3) (King and Boag, 2018), although this was not needed as acidosis began to correct. Hyperkalemia can also cause a peak T-wave (Harvey and Tasker, 2013), although the ECG reading was normal, and intravenous fluids were saline to avoid additional potassium. There is evidence to show that hypotension resuscitation using intravenous fluids can be contraindicated, particularly in cases of haemorrhage (King and Boag, 2018). Despite this, there are human studies that suggest using aggressive fluid resuscitation with a mean arterial pressure of less than 60 mmHg in cases of severe trauma until haemorrhage or trauma can be repaired (King and Boag, 2018).
Gelofusine was used to manage severe hypotension with hypovolaemia. Although colloids have been shown to cause acute kidney injury in patients (Byers, 2021), the clinical decision was made to try to continue a bolus of Gelofusine and attempt to combat the hypotension which may have caused further organ damage. Following the Gelofusine bolus, as an alternative Crumble was started on noradrenaline CRI to correct the hypotension. The noradrenaline CRI can help with increasing the mean arterial pressure, and it is suggested for use in sepsis patients (Mazzaferro and Wagner, 2001). However, there are risks of tachycardic arrythmias and vasoconstriction with noradrenaline (Mazzaferro and Wagner, 2001).
Alfaxalone was used as an anaesthetic induction agent. Campagna et al’s (2015) study showed alfaxalone induction has little impact on respiration. As alfaxalone has not got any analgesic properties it is vital that appropriate analgesia is administered (Duke-Novakovski et al, 2016). Intraoperatively CRI of fentanyl was used as the duration of effect is 20-30 minutes, which could be beneficial when stopping CRI (Duke-Novakovski et al, 2016). Monitoring an anaesthetic can be challenging, especially in emergency cases, making it important to utilise monitoring equipment. Capnography is a useful tool in anaesthesia, as well as in resuscitation of a patient (Welsh, 2009). In this case the patient was hypocapnic and despite attempts to rectify this with increased flow rates of O2 it stopped reading altogether. A sudden fall in ETCO2 can indicate cardiac arrest (Welsh, 2009), but further observations showed that the capnograph was failing to read.
Hypothermia is the most common postoperative problem (Welsh, 2009). This can have a detrimental impact on a patient, including arrhythmias, delays in drug metabolism and wound healing (Welsh, 2009). A cause of hypothermia can be hypotension (Welsh, 2009): a known concern in this case. As well as intravenous fluids and CRIs, warmed saline to lavage was used. This is suggested for lavage of the abdomen after urine in the abdomen (Ackerman, 2016). Warmed saline can help combat hypothermia, as well as warming intravenous fluids (Davies, 2012). Electrical fluid warmers are often used, but were unavailable in this case.
During recovery from anaesthetic and surgery, Crumble was monitored closely. It was particularly important to monitor urine output to ensure he could produce and pass urine (Welsh, 2009). In this case a urinary catheter was in situ meaning ins and outs of urine and fluid could be easily monitored and recorded on a chart (Table 1). The best method of collection is a closed urinary catheter system. This was used with a collection bag with a specifically designed tap at the bottom. Welsh (2009) suggests using this method. It is suggested to leave a urinary catheter in for 48 hours (Beiter, 2016), but in this case the catheter was removed after 24 hours as it was no longer needed. This was because the patient was very bright in the kennel. Blood tests were repeated before removing the urinary catheter to ensure Crumble was stable (Table 2). Crumble remained in hospital for 48 hours for further monitoring before discharge.
Table 1: Urine chart
| Time | Volume of urine produced | Urine mls/kg/hr | Volume of fluids given | Fluids mls/kg/hr | Total ins and outs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18:00 | 13.0 ml | 1.95 ml | 31.0 ml | 7.7 ml +CRI | +18.0 ml |
| 22:00 | 16.0 ml | 1.2 ml | - | - | - |
| 00:00 | 18.0 ml | 2.9 ml | 48.0 ml | 7.7 ml +CRI | +30.0 ml |
| 02:30 | 36.0 ml | 4.6 ml | 60.0 ml | 7.7 ml +CRI | +24.0 ml |
| 04:30 | 31.0 ml | 5.0 ml | 48.0 ml | 7.7 ml+CRI | +17.0 ml |
| 07:30 | 53.0 ml | 5.6 ml | 72.0 ml | 7.7 ml+CRI | +19.0 ml |
| 09:00 | 31.0 ml | 6.6 ml | 27.0 ml | 2.0 ml +CRI | -4.0 ml |
| 11:40 | 24.0 ml | 3.0 ml | 36.0 ml | 2.0 ml +CRI | +12.0 ml |
| 14:00 | 30.0 ml | 3.8 ml | 31.5 ml | 2.0 ml+CRI | +1.5 ml |
| 16:00 | 54.0 ml | 8.7 ml | 27.0 ml | 2.0 ml+CRI | -27.0 ml |
Table 2: Blood results
| Parameter | Time | Time | Time | Time | Time | Time | Time | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 09:00 15/4/21 | 10:30 | 12:10 | 14:25 | 15:50 | 19:15 | 02:50 16/4/21 | 14:45 | |
| pH | 7.062 | 7.07 | 7.14 | 7.16 | 7.16 | 7.26 | 7.37 | 7.42 |
| PCO2 | 6.61 | 54.1 | 46.7 | 39.2 | 40.5 | 33.6 | 30.1 | 31.0 |
| PO2 | 10.4 | 86.4 | 48.9 | 109.9 | 178.0 | 42.9 | 33.4 | 47.0 |
| HC03 | 14.1 | 15.7 | 16.0 | 14.2 | 14.7 | 15.2 | 17.5 | 20.3 |
| BE | -16.0 | -14.4 | -13.3 | -14.3 | -13.8 | -11.9 | -7.8 | -3.6 |
| S02 | 89.0 | 91.0 | 71.0 | 96.0 | 99.0 | 72.0 | 63.0 | 84.0 |
| TC02 | 16.0 | 16.9 | 16.9 | 15.1 | 15.6 | 15.8 | 17.8 | 20.4 |
| Lac | 2.46 | 2.25 | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.8 | 1.53 | 1.39 | 0.94 |
| Na+ | 158.0 | 147.0 | 150.0 | 147.0 | 150.0 | 148.0 | 142.0 | 151.0 |
| K+ | >12.0 | 5.7 | 5.3 | 6.5 | 5.5 | 4.5 | 4.6 | 3.7 |
| iCa | - | 1.12 | 1.21 | 1.11 | 1.14 | 1.17 | 1.21 | 1.18 |
| Ci | - | 122.0 | 126.0 | 128.0 | 130.0 | 127.0 | 121.0 | 121.0 |
| Haem | - | 48.0 | 49.0 | 51.0 | 52.0 | 48.0 | 32.0 | 24.0 |
| Hb | - | 16.5 | 16.8 | 17.3 | 17.6 | 16.3 | 10.8 | 8.3 |
| Glu | 12.5 | 15.5 | 9.2 | 4.8 | 4.8 | 8.3 | 10.2 | 6.9 |
| Crea | >1768.0 | 432.0 | 450.0 | 488.0 | 365.0 | 226.0 | 121.0 | 81.0 |
Conclusions
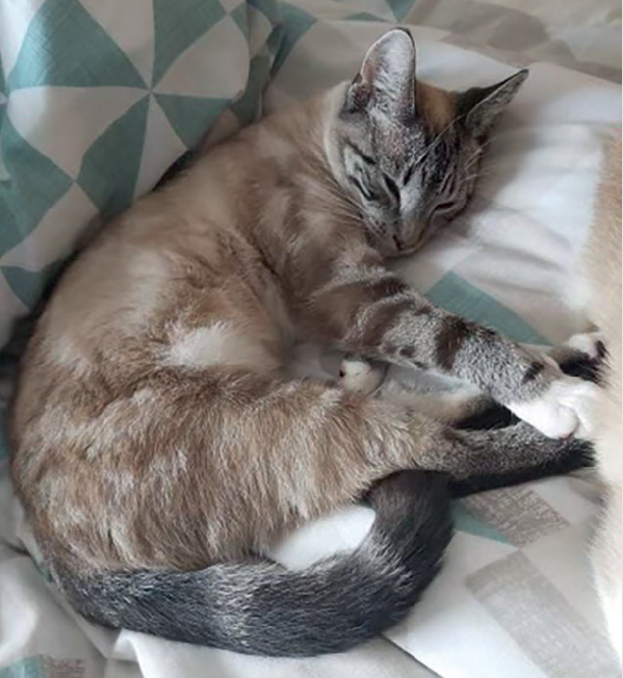
This case was challenging and educational with a rewarding outcome of Crumble recovering well and going home (Figure 3). It was managed well with the facilities and skills available in the practice. Rather than starting with a colloid to improve hypotension, noradrenaline may have been a better approach to reduce the risk of further acute kidney injury in an azotaemic patient. The urinary catheter ideally could have been managed more closely to remain in for longer to allow for further monitoring of urine output; however, it benefitted the patient making him more comfortable and playful in his kennel.

Key Points
- Management of hypotension can be performed with a multimodal approach.
- Hypothermia can be difficult to manage in surgical trauma cases.
- Multimodal analgesia is vital to help manage pain in ruptured bladders.
- Quick and thorough diagnostics from the veterinary surgeon and excellent anaesthesia management from the veterinary nurse played a key part in the success of this case.