References
Canine and feline hypertension
Abstract
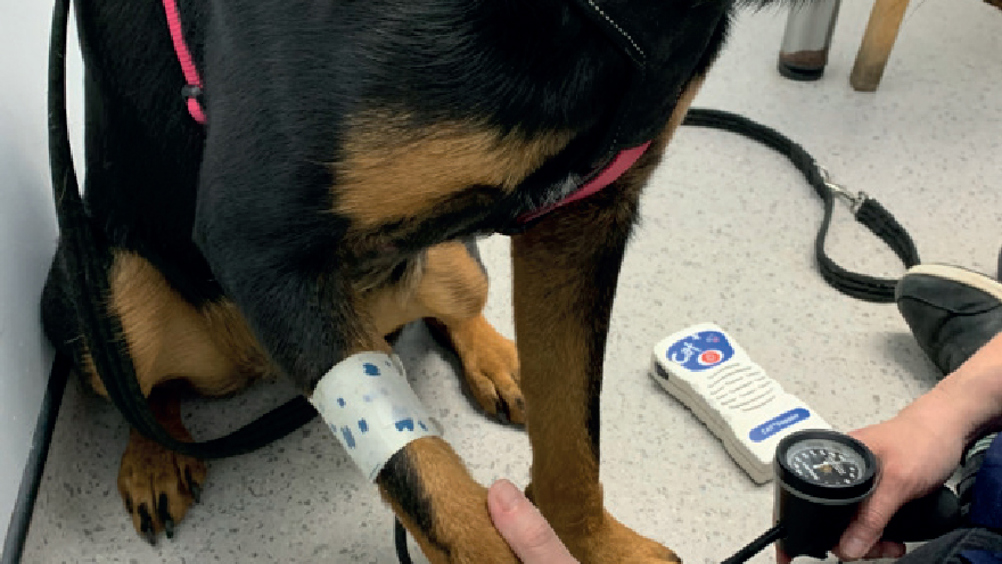
Systemic hypertension is a common finding in small animal practice. It has been classified into three groups: situational (or white-coat hypertension), primary or idiopathic, or secondary to another disease process. Secondary hypertension is the most common form, and chronic kidney disease the disease most reported to be associated with it. It is diagnosed using reliable and repeatable blood pressure measurements, and by excluding other causes. Treatment will vary depending on the underlying cause. Recent guidelines have suggested measuring blood pressure in dogs and cats at a senior life stage and performing a fundic examination in all animals with blood pressure more than 160 mmHg. Client education and regular screening are ways that veterinary nurses can help identify blood pressure changes and assess efficacy of antihypertensive medication.
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is widely reported in humans but is also commonly encountered in small animals. It may go undetected unless there are specific clinical signs, such as retinal detachment. Diagnosis and treatment are based on reliable and repeatable blood pressure measurements, which are usually carried out by a veterinary nurse. In busy practices with numerous time and pressure commitments, blood pressure is often not measured as regularly as it should be, and the number of cases is likely underestimated. Guidelines from both the American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine (ACVIM) and the International Society of Feline Medicine (ISFM) recommend regular screening of dogs and cats, particularly at senior life stage or if there is suspicion of target organ damage. Most commonly, hypertension is secondary to other disease process, such as chronic kidney disease, which may need to be treated alongside the hypertension. Nurses can play an important role in raising the profile of measuring blood pressure within practice and with clients.
Register now to continue reading
Thank you for visiting The Veterinary Nurse and reading some of our peer-reviewed content for veterinary professionals. To continue reading this article, please register today.

